Concussions are a specific type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that can occur when the head experiences a forceful impact, is bumped, or undergoes a sudden jolt. These events cause the brain to move rapidly inside the skull, potentially leading to various physiological changes and functional disruptions. Although concussions are commonly referred to as mild brain injuries, it is crucial to recognize their potential for significant symptoms and complications if not properly diagnosed and managed.
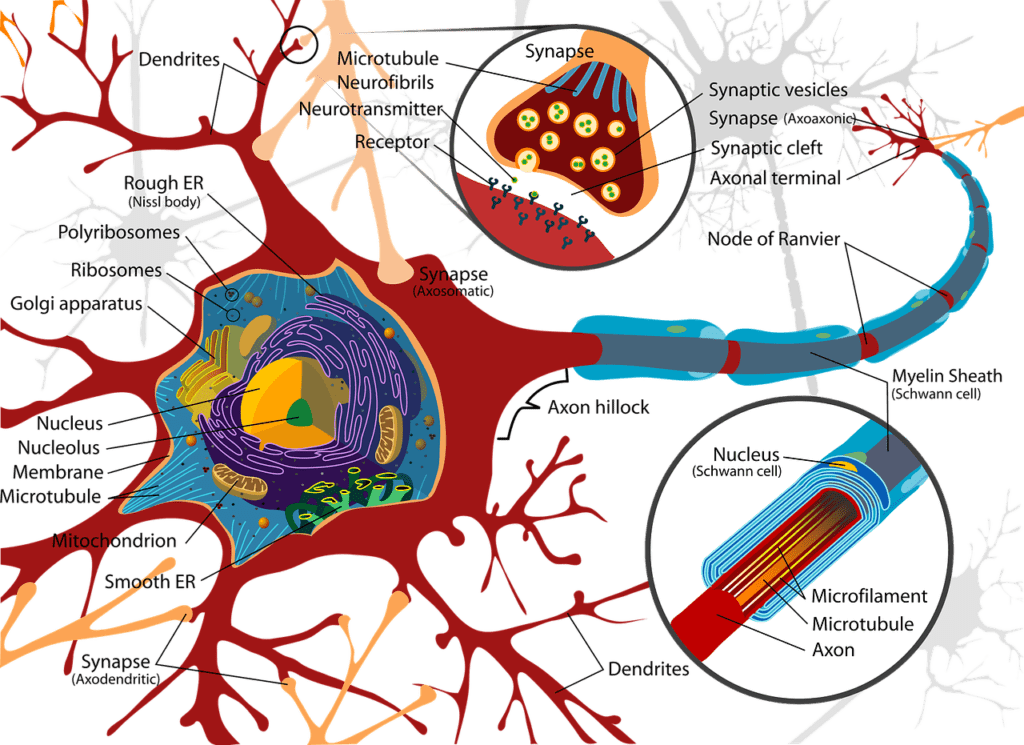
During a concussion, the brain undergoes complex processes that can disrupt its normal functioning. The impact or jolt causes the brain’s delicate tissues to stretch and twist, which can result in chemical changes and disturbances in neural communication. As a result, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that can affect various aspects of their physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being.
Metabolically, a concussion triggers a cascade of events within the brain. The initial impact can lead to an imbalance in the brain’s chemical environment. This disruption affects the release and regulation of various neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between brain cells. Additionally, the injury can disturb the brain’s energy metabolism and blood flow, further impacting its function.
Signs and symptoms:
- Headache or pressure in the head
- Dizziness or change in balance
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Confusion or feeling foggy (brain fog)
- Slowed reaction time
- Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
- Change in digestion and/or GI function
- Vision changes
- Easily overly stimulated
- Irritability or mood changes
- Sleep disturbances
Recovery:
Understanding the physical and metabolic processes involved in a concussion helps to highlight the importance of proper diagnosis, management, and recovery. It underscores the need for rest, gradual return to activities, and appropriate medical guidance to ensure the brain has sufficient time and support to heal.
Following a concussion, the brain enters a complex recovery process. It requires time and rest to heal and restore its normal functioning. During this recovery period, it is common for individuals to experience a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional symptoms. These can include headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, mood changes, and sensitivity to light or noise.
Most people recover from a concussion within 7 to 10 days with proper rest and management of symptoms. However, some people may experience symptoms for weeks or even months, a condition known as post-concussion syndrome (PCS). PCS is diagnosed when the symptoms of concussion persist.
post-concussion syndrome:
Conclusion:
If you or someone you know has experienced a concussion or is struggling with post-concussion symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional support. Together, we can work towards restoring well-being and promoting a successful recovery.
As an occupational therapist specializing in concussion management, I am dedicated to helping individuals navigate the challenges of concussion recovery. By providing comprehensive assessment, personalized treatment plans, and evidence-based interventions, I strive to support individuals in their journey towards recovery and a return to their normal activities and passions.
Note: This blog post provides educational information and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.




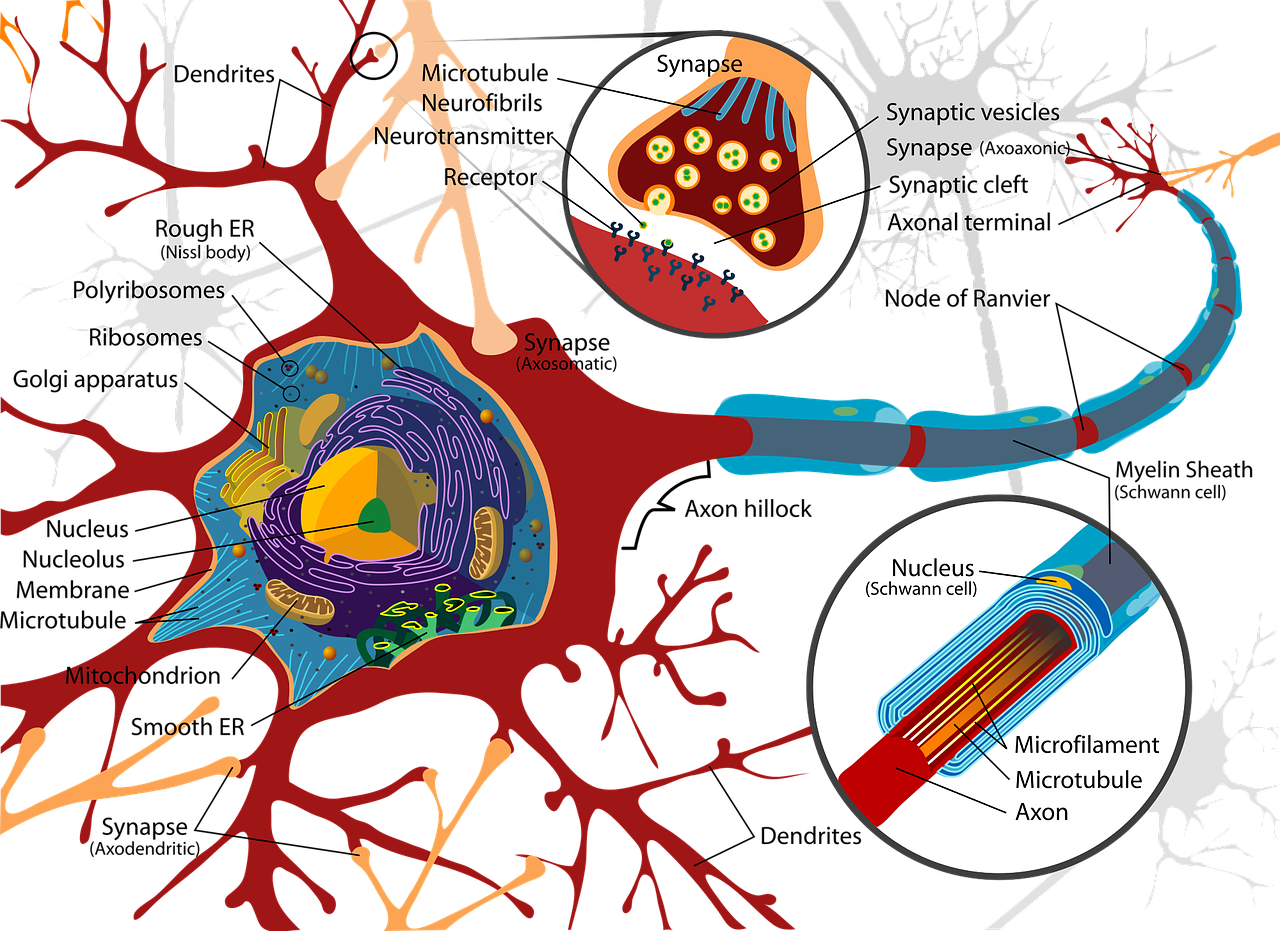
Pingback: Digging deeper into brain injury: The Neurochemical Cascade of Concussion – Evergreen Body Balance